REST风格 初识REST Restful就是一个资源定位及资源操作的风格。不是标准也不是协议,只是一种风格。基于这个风格设计的软件可以更简洁,更有层次,更易于实现缓存等机制。
比如说,我们以前在进行开发的时候,通常一个请求是:http://localhost:8888/user/getUser?id=1
在这个请求中,getUser是方法名,一个动词,我们要根据这个动词去进行相应的操作,换句话说,这个为名id的用户,它的资料存在这个一个getUser方法中。从现实中来看,这是不科学的,一个用户怎么会存在一个动词当中,一个用户应该使用: http://localhost:8888/user/1 来表达才比较对,user代表了这个群体是一个用户,1表示了这个用户的id。
基于这种思想,就诞生了一个名为:REST的风格。这种规范自2000年以来,开始流传于世间。
构建REST风格网站 引入依赖 在构建过程中,除了前面必要的依赖,如mysql、mybatis之外,还需要引入一个人依赖:
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId > </dependency >
有了这个依赖,才能实现对页面的处理,首先看一个例子:
页面之间的跳转 我们在controller中先写入这一段代码:
1 2 3 4 5 @GetMapping ("/index" )public String index () return "index" ; }
这一段代码表示,接收一个index请求,并且会返回一个为名index的字符串。看起来是这样的,但实际上,它在引入了thymeleaf依赖之后,会自动在String后面拼串,返回的是一个名为 index.html的页面。
同时,也需要在 resource的templates包中,放入index的页面,它就能够识别,且自动跳转。
同时,你还要学习关于计算机网络和HTTP相关的知识,至少要知道一下几点:
POST:一般是用于提交数据的
GET:一般是用于获取数据的
PUT:一般是用于更新一条数据的
DELETE:一般是用于删除数据的
PATCH:一般是用于更新一批数据的
实体类 为了使得出入的数据都能被完全的转移至数据库,通常需要以下几个实体类:
用于传入数据库的user:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Data @Alias ("user" )public class User private Long id; private String userName; private SexEnum sex = null ; private String note; }
前端传进来的user:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Data public class UserVo private Long id; private String userName; private int sexCode; private String sexName; private String note; }
在controller层中,需要添加的方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 private User changeToPo (UserVo userVo) User user = new User(); user.setId(userVo.getId()); user.setUserName(userVo.getUserName()); user.setSex(SexEnum.getSexEnum(userVo.getSexCode())); user.setNote(userVo.getNote()); return user; } private UserVo changeToVo (User user) UserVo userVo = new UserVo(); userVo.setId(user.getId()); userVo.setUserName(user.getUserName()); userVo.setSexCode(user.getSex().getCode()); userVo.setSexName(user.getSex().getName()); userVo.setNote(user.getNote()); return userVo; } private List<UserVo> changeToVoes (List<User> poList) List<UserVo> voList = new ArrayList<>(); for (User user : poList) { UserVo userVo = changeToVo(user); voList.add(userVo); } return voList; } @Data public class ResultVo public ResultVo (Boolean success, String message) this .success = success; this .message = message; } private Boolean success = null ; private String message = null ; }
配置文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 server: port: 8888 mybatis: mapper-locations: classpath:/mapper/*Mapper.xml type-aliases-package: com.example.rest.pojo type-handlers-package: com.example.rest.typeHandler spring: datasource: username: root password: 123456 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springtest?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver tomcat: max-idle: 10 max-wait: 10000 max-active: 50 initial-size: 5
MyBatis的xml配置 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" > <mapper namespace ="com.example.rest.dao.UserDao" > <select id ="getUser" parameterType ="long" resultType ="user" > select * from t_user where id = #{id} </select > <insert id ="insertUser" useGeneratedKeys ="true" keyProperty ="id" parameterType ="user" > insert into t_user(user_name, note) values(#{userName}, #{note}) </insert > <update id ="updateUser" > update t_user <set > <if test ="userName != null" > user_name =#{userName},</if > <if test ="note != null" > note =#{note}</if > </set > where id = #{id} </update > <select id ="findUsers" resultType ="user" > select id, user_name as userName, note from t_user <where > <if test ="userName != null" > and user_name = #{userName} </if > <if test ="note != null" > and note = #{note} </if > </where > </select > <delete id ="deleteUser" parameterType ="long" > delete from t_user where id = #{id} </delete > </mapper >
为了不多赘述,以下省略mybatis、mysql、typeHandler和enum的配置。
controller层 添加json数据至数据库 先贴controller层的设计:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @RestController public class UserController @Autowired private UserService userService = null ; @GetMapping ("/index" ) public String index () return "index" ; } @PostMapping ("/user" ) public User insertUser (@RequestBody UserVo userVo) User user=this .changeToPo(userVo); return userService.insertUser(user); } }
这里使用的是PostMaping,表示我们所接受到的是Post请求,这里在UserVO使用@RequestBody,目的是表示这里接受的必须是json型数据,也之后json型数据才会被绑定到UserVo当中。
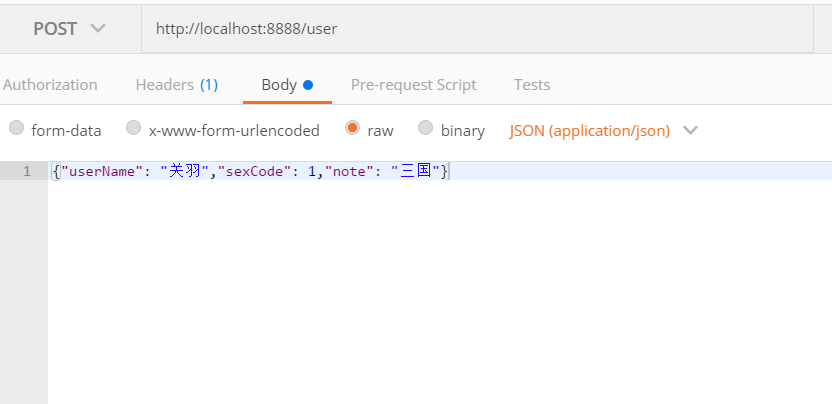
然后在使用转换,在传入数据库当中,这里打开PostMan开始测试:
传入的是json型数据,可以发现,这里在URL并没有使用任何的动词,而是直接传入json数据到后端。
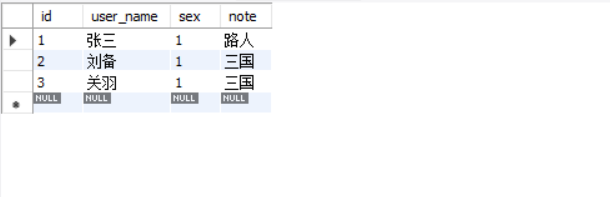
看看数据库:
这显然成功了。
获得数据库信息 我们继续在controller中添加数据:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @GetMapping (value = "/user/{id}" )@ResponseBody public UserVo getUser (@PathVariable("id" ) Long id) User user = userService.getUser(id); return changeToVo(user); }
这里我们看到,使用的是@PathVariable,这是什么意思呢?这表示我们的id字段将会从url中获取,于是id变获得了,{id},可能你会提问,我使用:?id=1,不是也可以吗?当然可以,但是当你传入多个参数的时候,就会变的很麻烦,别着急,往下看。
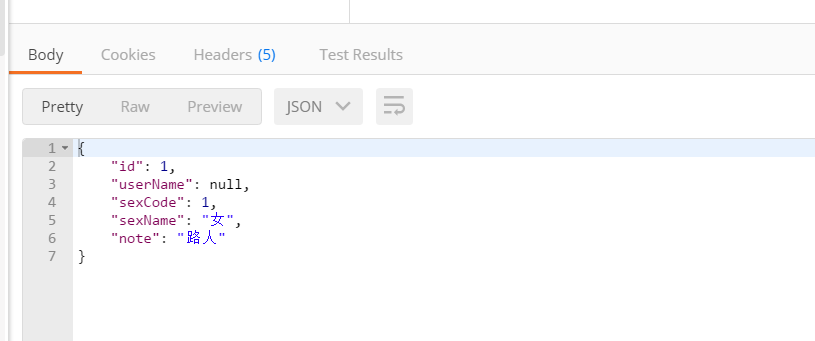
在看看是否从数据库获取成功:
输入: http://localhost:8888/user/1
我们发现,这次没使用所谓的getUser,也获得了数据。但是你看,这里userName居然是空的?
我回去看看数据库,原来数据库设置用户名是user_name,而我们设计的类是userName,这不一样,但是没关系,我们可以在yml配置文件中的mybatis配置中加一句:configuration: map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
这样它就会开启驼峰命名法,会自动将大写转化为 _ 加 小写 ,这样在映射数据库中,就成功把userName转化为user_name了。
查询符合要求的用户 在查询符合要求的用户时,为了节省查询量,肯定需要传入多个关键词,比如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @GetMapping ("/users/{userName}/{note}/{start}/{limit}" )@ResponseBody public List<UserVo> findUsers ( @PathVariable("userName" ) String userName, @PathVariable ("note" ) String note, @PathVariable ("start" ) int start, @PathVariable ("limit" ) int limit) { List<User> userList = userService.findUsers(userName, note, start, limit); return this .changeToVoes(userList); }
可以看到的是,我们传入了多个关键词就只用/分割开就行了,不需要传入id=1&username=“xxx”,这么麻烦了,这就是 @PathVariable的作用。
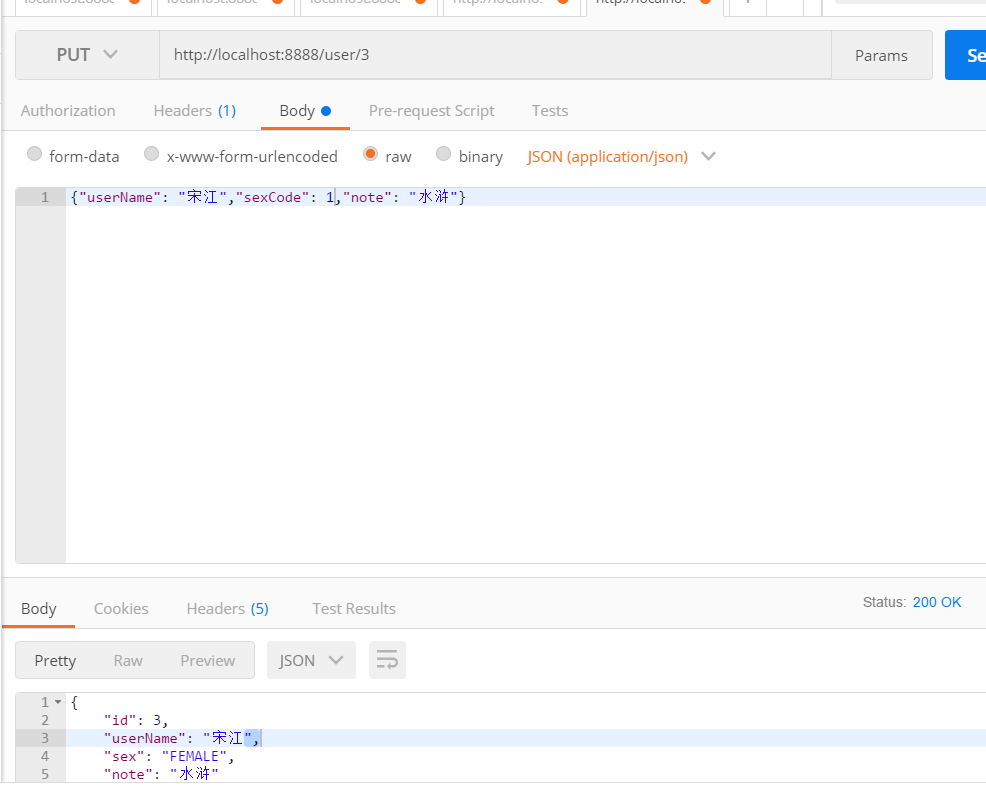
修改用户数据 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @PutMapping ("/user/{id}" )@ResponseBody public User updateUser (@PathVariable("id" ) Long id, @RequestBody UserVo userVo) User user = this .changeToPo(userVo); user.setId(id); userService.updateUser(user); return user; }
可以看到,这里将两个注解结合到了一起,使用在这个url中,修改所需要的修改的用户:
看,这样就好了,即在url中选择了用户id,又在json中传达了需要的数据,并且又避免了动词的存在,一举三得。再看看数据库:
其他测试 其他数据测试也是几乎一样的,这里仅提供代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 @PatchMapping ("/user/{id}/{userName}" ) @ResponseBody public ResultVo changeUserName (@PathVariable("id" ) Long id, @PathVariable ("userName" ) String userName) { int result = userService.updateUserName(id, userName); ResultVo resultVo = new ResultVo(result>0 ,result > 0 ? "更新成功" : "更新用户【" + id + "】失败。" ); return resultVo; } @DeleteMapping ("/user/{id}" )@ResponseBody public ResultVo deleteUser (@PathVariable("id" ) Long id) int result = userService.deleteUser(id); ResultVo resultVo = new ResultVo(result>0 , result > 0 ? "更新成功" : "更新用户【" + id + "】失败。" ); return resultVo; } @PatchMapping ("/user/name" )@ResponseBody public ResultVo changeUserName2 (Long id, String userName) int result = userService.updateUserName(id, userName); ResultVo resultVo = new ResultVo(result>0 , result > 0 ? "更新成功" : "更新用户名【" + id + "】失败。" ); return resultVo; }
代码补充 性别的枚举:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public enum SexEnum {
其实并不长,之所以看起来长,是因为枚举类型不能使用@Data。
SexTypeHandler:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 @MappedTypes (SexEnum.class ) @MappedJdbcTypes (JdbcType .INTEGER ) public class SexTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler <SexEnum > @Override public SexEnum getNullableResult (ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException int code = rs.getInt(columnName); return SexEnum.getSexEnum(code); } @Override public SexEnum getNullableResult (ResultSet rs, int index) throws SQLException int code = rs.getInt(index); return SexEnum.getSexEnum(code); } @Override public SexEnum getNullableResult (CallableStatement cs, int index) throws SQLException int code = cs.getInt(index); return SexEnum.getSexEnum(code); } @Override public void setNonNullParameter (PreparedStatement ps, int index, SexEnum sex, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException ps.setInt(index, sex.getCode()); } }
学点前端 闭门造车,不是明智之选,看点前端知识:
为了在前端也能够识别且使用thymleaf语法,需要在页面顶部添加:
1 <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thymeleaf.org" >
为了能使用JQuery库,需要添加:
1 <script type ="text/javascript" src ="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.2.1.min.js" > </script >
JavaScript和JQuery的区别就像,C++和STL类库的区别,int和Integer的区别,面粉和蛋糕的区别。
学一下JS:
在前面的使用post请求时,也可以在页面这么使用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 <script type ="text/javascript" > function post () var params = { 'userName' : 'user_name_new' , 'sexCode' : 1 , 'note' : "note_new" } $.post({ url : "./user" , contentType : "application/json" , data : JSON .stringify(params), success : function (result) if (result == null || result.id == null ) { alert("插入失败" ); return ; } alert("插入成功" ); } }); } post(); </script >
这样便可以在前端执行JS代码。运行这个页面的时候,会触发post函数,post函数开头便定义了一个值,这个值是json类型,并且会执行$.post方法,它可以这么写是因为JQ的原因,从传达的url中获取要接收的json参数,成功则执行函数,并返回成功的消息框,否则会在页面返回插入失败的消息框。OK。
项目地址:https://github.com/Antarctica000/SpringBoot/tree/master/rest